 需要考量ESD保护的系统。
需要考量ESD保护的系统。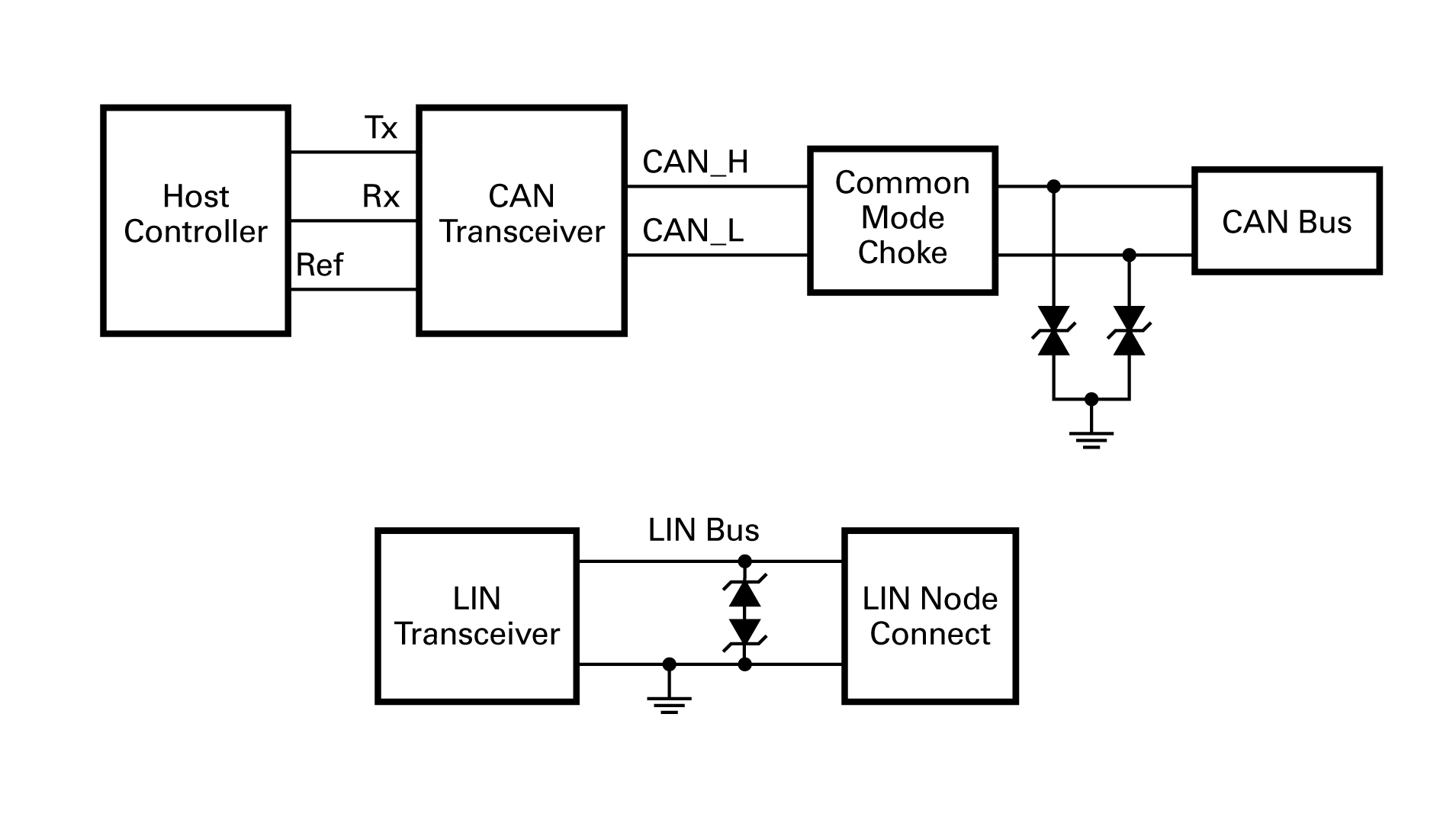 CAN和LIN公交车的保护方案图解。
CAN和LIN公交车的保护方案图解。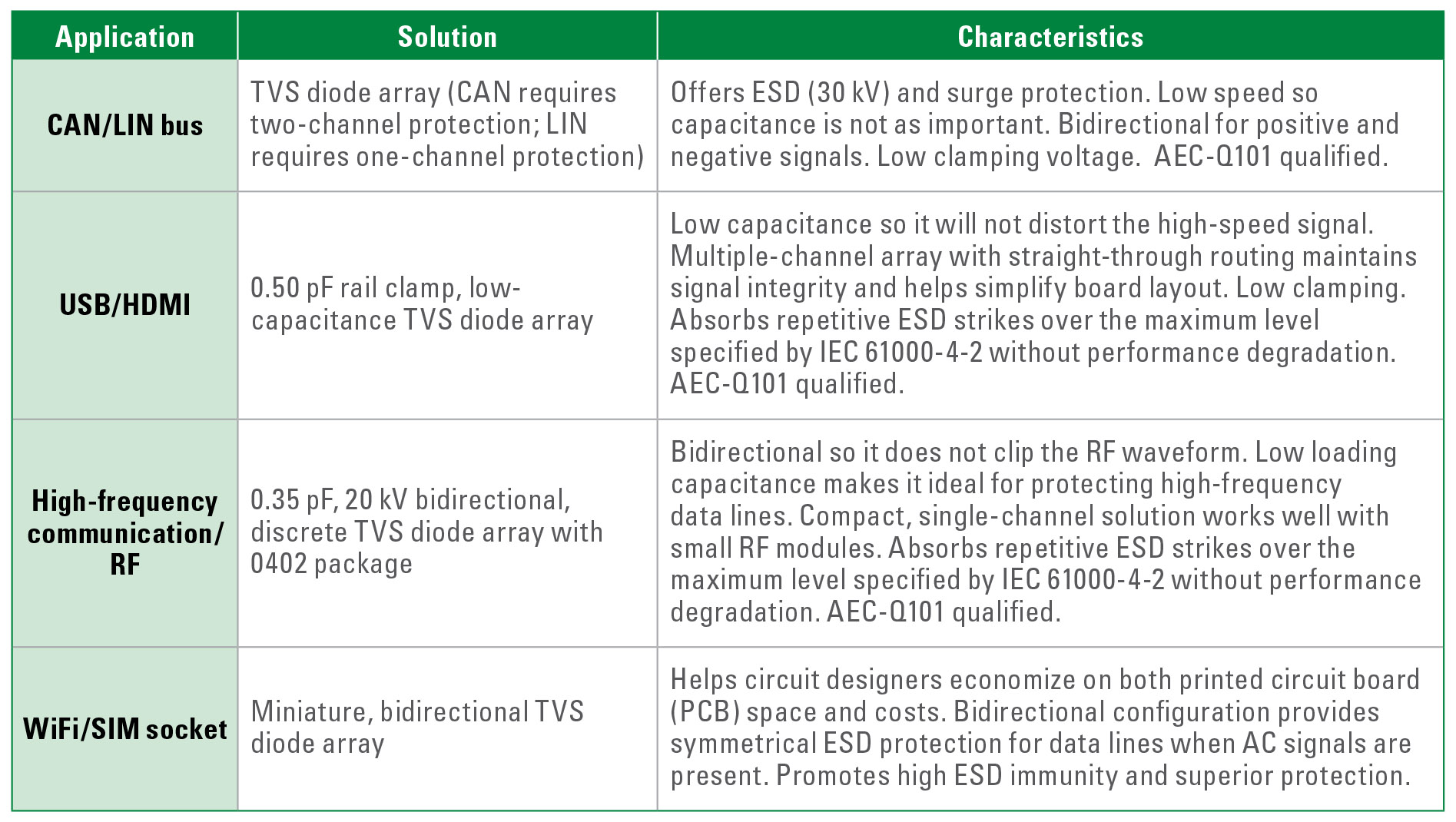 汽车电路保护方案的特点。
汽车电路保护方案的特点。 Littelfuse生产的该款SM24CANA TVS二极管阵列能够保护CAN公交车。
Littelfuse生产的该款SM24CANA TVS二极管阵列能够保护CAN公交车。 Littelfuse生产的该款TPSMA6L系列TVS二极管提供了小范围需要的电气性能。
Littelfuse生产的该款TPSMA6L系列TVS二极管提供了小范围需要的电气性能。 James Colby是Littelfuse有限公司的半导体业务发展经理,负责定位并开发战略增长市场,以及将新产品推广到这些市场。他拥有南伊利诺伊大学(Southern Illinois University)电气工程理学士学位,和凯勒管理研究生院(Keller Graduate School of Management)的MBA学位。他在Littlefuse公司有15年以上的工作经验,在电子设备行业有超过23年的从业经验。
James Colby是Littelfuse有限公司的半导体业务发展经理,负责定位并开发战略增长市场,以及将新产品推广到这些市场。他拥有南伊利诺伊大学(Southern Illinois University)电气工程理学士学位,和凯勒管理研究生院(Keller Graduate School of Management)的MBA学位。他在Littlefuse公司有15年以上的工作经验,在电子设备行业有超过23年的从业经验。
过去十年,随着新技术的演进,汽车电子设备的安全性和可靠性标准也有了很大改变。许多以前消费者购买汽车时作为选配的技术,包括稳定性控制和防抱死制动系统等,现在都已经是大多数车辆的标配。而车道偏离警告系统,车辆通信系统和夜视镜等新型电子设备则成为可选配的新款电子设备。
随着汽车设计与制造各方面的要求不断提升,设计师们必须充分了解汽车认证标准方面的要求,而且这些要求比消费者电子产品的保护要求涵盖范围更广。但是,在设计要能够符合标准则面临了诸多技术挑战。
虽然集成电路因其体积更小,速度更快在汽车中被使用,但却更容易遭受静电放电(ESD)的损害。在认证测试过程中通过仿真实验,我们有针对的模拟电气瞬变的车真实场景,来测试这些设备是否达标。
本文旨在提供汽车标准和电路的实际应用和解决方案,目的是帮助电路设计师们实现稳健、可靠的设计。首先,本文会强调两种测试标准的测试要求,并探讨需要保护的汽车电路的最常见类型。然后,本文会解释先进的电路保护技术,用于保护多种汽车应用,并且这些技术应纳入早期设计阶段,以确保安全性和可靠性。
符合汽车测试标准
为了保证先进的车辆电子设备可以合格上市,电路设计师们必须充分了解ISO 10605和AEC-Q101的测试标准要求。
ISO 10605: 该国际标准详细说明了为公路用车研发的电子模块评估的ESD测试方法。所有模块必须能够抵抗由装配,保养/维修,和操作引起的电干扰。对于ISO10605合规来说,每个电路和模块必须在装配到车内之前进行预先测试。汽车装配完毕后,也必须经过测试,以确保安全性和可靠性。
AEC-Q101: ISO 10605着重于电气危害,而AEC-Q101则关于环境的具体要求。该标准详述了一系列合格性测试,目的是确保基于半导体的汽车部件的长期可靠性。ESD保护装置,诸如瞬态电压抑制(TVS)二极管,以及TVS二极管阵列,必须符合AEC-Q101标准,这样汽车制造商才能将它们装配到车内。AEC-Q101的合规部件必须能经受热冲击和热循环,极端温度,以及高湿度环境。
明确需要保护的汽车电路
所有电路和部件都容易遭受电磁瞬变的损害——这一点与它们在车辆内部的装配位置无关。以下列举了四个最常见的需要保护的电路:
1. 老式双路通信公交车:
a. 控制器局域网络(CAN):该标准允许微控制器和装置实现车内通信,而无需使用主机。CAN系统具有多种功能——从动力转向到发动机计算机和变速器之间的重要的传动系统通信。
b. 局域互联网络(LIN):该串行网络协议用于车内部件间的通信。LIN公交车具有简单的电机功能,诸如移动电动座椅,以及开关恒速操纵器。
CAN/LIN公交车有更高的瞬时突波发生概率,可能会造成未受保护的CAN/LIN无线电收发机故障。图2刻画了CAN和LIN公交车保护的实用策略。
2. 高速数字公交车:USB/HDMI接口支持的车内消费者应用。例如,仪表板或许会有一个USB接口,乘客可以用它为手机/平板电脑充电或者播放音乐。HDMI接口是备用接口,也可用于连接车内前视摄像头。这些接口的数据流量越来越快,芯片敏感性越来越高,因此需要卓越的信号完整性和系统可靠性。USB/HDMI接口可能会因车内的相对小型ESD事件和短路而遭到损坏。
3. Wi-Fi通信/SIM卡槽:该技术允许车辆为乘客提供蜂窝3G或LTE通信。SIM模块是电路的中介部分,能将LTE转换成Wi-Fi,用户可以连接手机、平板电脑和笔记本电脑。SIM卡槽需要ESD保护,因为在模块装载或替换到车内时,卡槽易受人类活动的影响。
4. 高频通信/RF(无线射频):该技术由短程RF电路支持,可以实现车对车或车对路通信。网络可以让车辆发现彼此,并实现相互通信,有助于防止碰撞事故的发生,也有利于建设智能交通系统。RF放大器的前端对ESD非常敏感。无偏差RF信号能够在天线电路上产生正负极性电压。
匹配电路保护方案和汽车应用
汽车电路设计师们或许很难获得高质量的电路保护方案,因为有能力研发满足AEC-Q101标准的产品的公司屈指可数。在选择汽车制造商时,务必要验证该制造商的资质证书,以确保该公司的产品满足所有产业适用标准。该公司也应该遵守产品设计的最佳实践,并应用高质量制造工艺。表1列出了一些电路保护方案,都应在早期设计阶段实施。
结论
稳健的汽车电子设备设计要求提前规划环境和电气危害管理。成功的设计始于对ISO 10605和AEC-Q101测试标准要求的充分理解。每一个应用层的电子设备都需要充分的保护,因为整车及其中的每一个模块都会经过全面的可靠性测试。
电路设计师也应该考量需要保护的汽车电路的电气脆弱性,尤其是与新型通信和网络相关的电路。通过了解汽车测试的标准和电路,设计师们就能够选择可以为其所用的最佳电路保护方案。
本文由来自Littelfuse有限公司James Colby为《汽车工程杂志》撰稿。
作者:James Colby
来源:SAE《汽车工程杂志》
翻译:SAE上海办公室
Understanding the Importance of electrostatic discharge standards
Within the past decade, the safety and reliability standards for automotive electronics have changed significantly as new technologies have evolved. Technologies that used to be sold as options, including stability control and antilock brakes, are now offered as standard features in most vehicles. Today’s innovative automotive electronics enable lane-departure warning, vehicle communications, and night vision.
This shift in design and manufacturing mandates that designers understand the demands of the automotive certification standard that extends beyond the protection requirements for consumer electronics. However, designing for the automotive standard involves several technology challenges.
As automotive integrated circuits continue getting smaller and faster, they become more susceptible to damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD). In addition, the automotive environment is marked by harsh electrical transients, which are simulated during automotive certification testing.
This article makes practical application of automotive standards, circuits, and solutions to help circuit designers create robust, reliable designs. First, it highlights the testing requirements of two test standards and discusses the most common types of automotive circuits requiring protection. Then, it identifies advanced circuit protection technologies for several automotive applications that should be implemented early in the design phase to ensure safety and reliability.
Measuring up to automotive test standards
Circuit designers must consider the requirements of the ISO 10605 and AEC-Q101 test standards for their advanced vehicle electronics to be qualified for the automotive market.
ISO 10605: This international standard specifies ESD test methods for evaluating electronic modules developed for use in road vehicles. The modules must be able to manage electrical disturbances caused by assembly, maintenance/repair, and operation. For ISO 10605 compliance, every circuit and module must be pretested before being added to the vehicle. Once the assembled car is ready, it must also be tested to ensure safety and reliability.
AEC-Q101: While ISO 10605 focuses on electrical hazards, AEC-Q101 is an environmental specification. It describes a series of qualification tests that ensure the long-term reliability of semiconductor-based components in the automobile. ESD protection devices such as transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes and TVS diode arrays must increasingly conform to the AEC-Q101 standard for a vehicle manufacturer to add them to a vehicle. AEC-Q101-compliant components must be able to handle thermal shock and cycling, extreme temperatures, and high humidity.
Identifying automotive circuits requiring protection
All circuits and components are susceptible to damage from electrical transients—regardless of their location within the vehicle. The following list identifies the four most common circuits requiring protection:
1. Legacy two-wire communication buses:
a. Controller Area Network (CAN): This standard allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate within a vehicle without the use of a host computer. CAN systems handle a variety of functions—from power steering to the critical drive-train communications between the engine computer and the transmission.
b. Local Interconnect Network (LIN): This serial network protocol is used for communication between components in the vehicle. LIN buses manage simple electromechanical functions such as moving the power seats and toggling the cruise control.
CAN/LIN buses have a high chance of transient surge exposure, which can cause unprotected CAN/LIN transceivers to fail. Figure 2 illustrates practical strategies for CAN and LIN bus protection.
2. High-speed digital buses: USB/HDMI ports support consumer applications within the vehicle. For instance, the dashboard may contain a USB port for passengers to charge their phone/tablet or play music. HDMI ports are also being used for backup and forward-looking cameras in vehicles. With faster throughput and greater chip sensitivity, these ports require outstanding signal integrity and system reliability. USB/HDMI ports could be damaged by relatively small ESD events and short circuits within the automobile.
3. Wi-Fi communication/SIM socket: This technology allows the vehicle to offer cellular 3G or LTE communication to the passengers. The SIM module is the intermediary part of the circuit that will convert LTE to Wi-Fi, allowing users to connect to phones, tablets, and laptops. The SIM socket requires ESD protection because it will be subjected to human interactions when the module is installed or replaced in the vehicle.
4. High-frequency communication/RF (radio frequency): This technology is supported by short-range RF circuits that enable vehicle-to-vehicle or vehicle-to-road communications. The network allows cars to see each other and communicate from vehicle to vehicle, which may help prevent collisions and enable smart traffic systems. The front ends of the RF amplifiers tend to be very sensitive to ESD. Unbiased RF signals will generate positive and negative polarity voltages on the antenna circuit.
Matching circuit protection solutions to automotive applications
Automotive circuit designers may struggle to find high-quality circuit protection solutions since the number of companies that are capable of developing products that meet the AEC-Q101 standard is limited. When selecting a manufacturer, it is vital to verify the company’s certifications to ensure that its products meet all applicable industry standards. The company should also follow best practices in product design and utilize high-quality manufacturing processes. Table 1 identifies several circuit protection solutions that should be implemented early in the design phase:
Conclusion
Designing robust automotive electronics requires advance planning for the management of environmental and electrical hazards. Successful design starts with understanding the requirements of the ISO 10605 and AEC-Q101 test standards. Adequate protection is required at each layer of electronics since individual modules as well as the completed car will be fully tested for reliability.
The circuit designer should also consider the electrical vulnerabilities of the automotive circuits requiring protection, especially those involving innovative communications and networking. With an understanding of automotive test standards and circuits, the designer can choose the best circuit protection solution for his or her application.
This article was written for Automotive Engineering by James Colby of Littelfuse, Inc.
Author: James Colby
Source: SAE Automotive Engineering Magazine
等级
打分
- 2分
- 4分
- 6分
- 8分
- 10分
平均分
- 作者:James Colby
- 行业:汽车
- 主题:安全性人体工程学/人因工程学电气电子与航空电子
